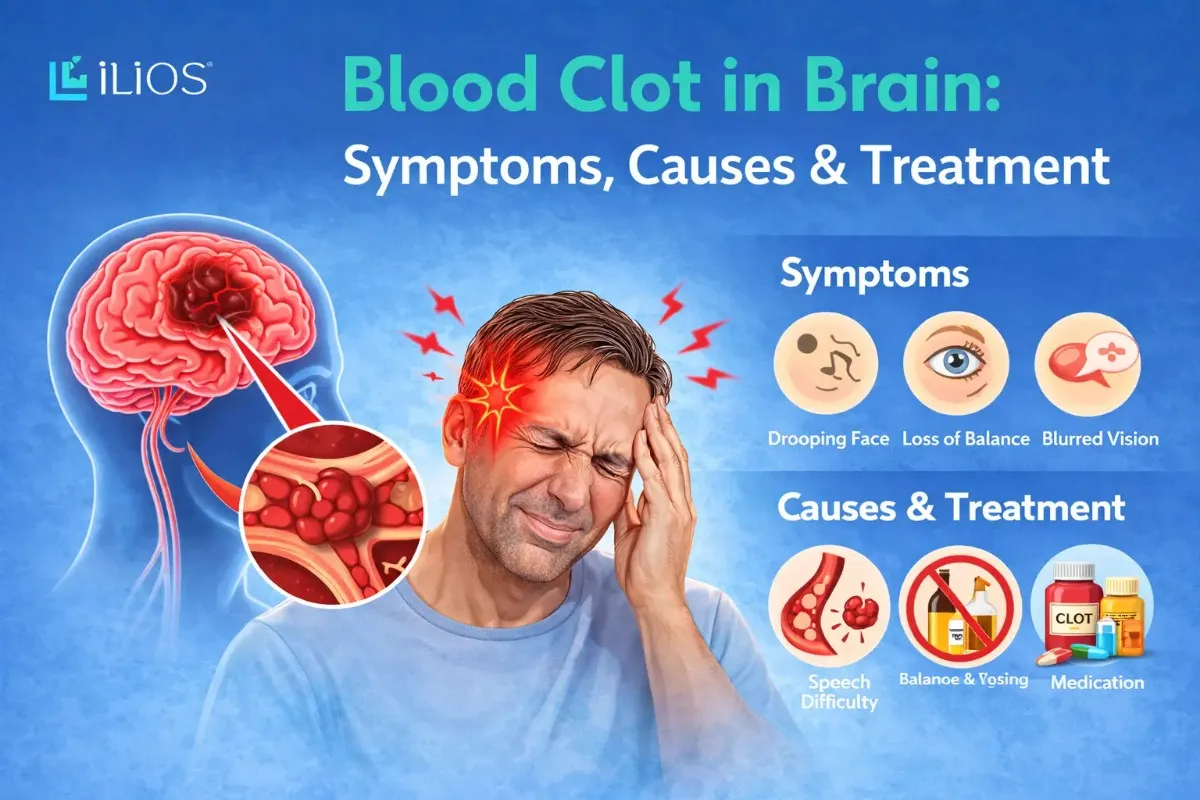
A blood clot in brain is a serious medical condition that may disrupt the normal flow of oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue and may result in complications, which could be fatal. Many people refer to this problem as a certain type of stroke that can strike suddenly and worsen rapidly; thus, it requires early recognition. Certain risk factors associated with high blood pressure, obesity, smoking, heart diseases, and disorders of clotting-impaired clothing increase the chances of its incidence.
Determining blood clot in brain symptoms, causes, and treatment options can make all the difference in outcomes. From sudden severe headaches, along with problems with vision, to difficulty speaking or even weakness on one side of the body, these warning signs should never go unnoticed. Prompt diagnosis and immediate medical intervention reduce brain damage and improve the chances of blood clot in brain recovery.

Serious About Your Health? We Are Too.
Partner with India's fastest-growing diagnostic network for precision testing.
What is Blood Clot in Brain?
A blood clot in brain is a serious health condition that is characterised by the reduction of the flow of blood to a section of the brain that has been blocked. It is alternatively known as cerebral thrombosis. Cerebral thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in any of the vessels of the brain. According to the presentation of the cause and the effect of the condition that is known as the brain clot in brain symptoms, the condition is classified as a stroke. Stroke is classified into two types: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
In an ischemic stroke, a blockage in an artery that carries oxygenated blood to the brain occurs. The result of this blockage is that brain cells become weakened and eventually perish. Whereas, a Herorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, which leads to bleeding inside or around the brain. While Ischemic strokes are caused by clots, Hemorrhagic strokes result from ruptured vessels, but both can cause brain injury.
Moreover, brain cells are sensitive to oxygen deprivation! Damage can begin within just a few minutes after blood is interrupted. Without prompt blood clot in brain treatment, brain cells continue to die rapidly, increasing the risk of permanent disability or even death. However, immediate medical care is necessary to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
What are the Common Symptoms of Blood Clot In Brain?
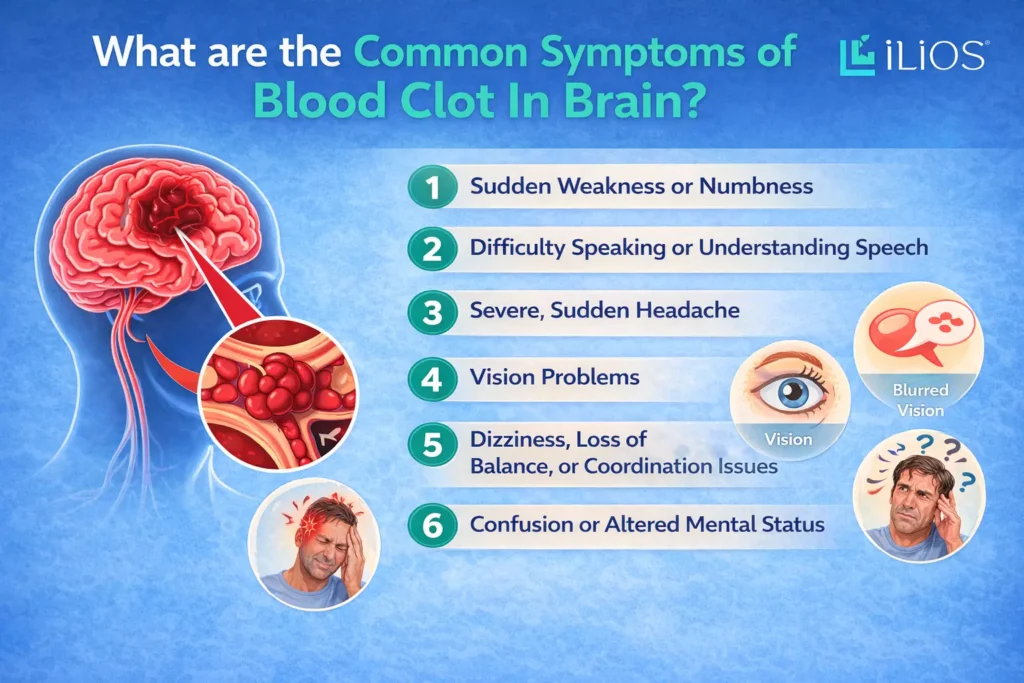
1. Sudden Weakness or Numbness
A common symptom of suffering from a clot is feeling that the face or the arm or the leg is suddenly weak or is even paralysed. You may feel that your face is drooping, that your arm is not being lifted, or that you are having difficulty balancing your body while walking. A blood clot in the brain blocks blood flow to the part of the brain that processes sensations.
2. Difficulty Speaking or Understanding Speech
A blood clot in the brain can affect areas responsible for language! Suddenly, it could be slurred speech, incoherent talking, difficulty with finding specific words, and even an inability to understand the main idea. It could begin suddenly and require treatment as a medical emergency.
3. Severe, Sudden Headache
A severe headache that comes on abruptly and feels unlike typical headaches is a serious warning sign. It’s often described as the “worst headache ever,” and may be accompanied by vomiting, nausea or neck stiffness. A prompt medical evaluation, including imaging studies reviewed by a Radiology Second Opinion Doctor, can quickly help confirm the diagnosis.
4. Vision Problems
Blurred vision, sudden loss of vision, or double vision in one or both eyes can be warning signs of a disruption of blood supply to the visual centres of the brain. Partial blindness or loss of sharpness of vision, which may develop within minutes, may also occur in some.
5. Dizziness, Loss of Balance, or Coordination Issues
He or she may suddenly become unsteady, dizzy, or unable to coordinate movements. Difficulty walking, loss of balance, or frequent falls may also occur when a clot involves the cerebellum or brainstem, which are structures that organise posture and balance.
6. Confusion or Altered Mental Status
Sudden confusion, memory problems, disorientation, or unusual behaviour may signal a blood clot in the brain. The individual may look ‘foggy’ in their mind and may not react appropriately or could even be unconscious.
Key Reasons for Blood Clot in Brain To Determine
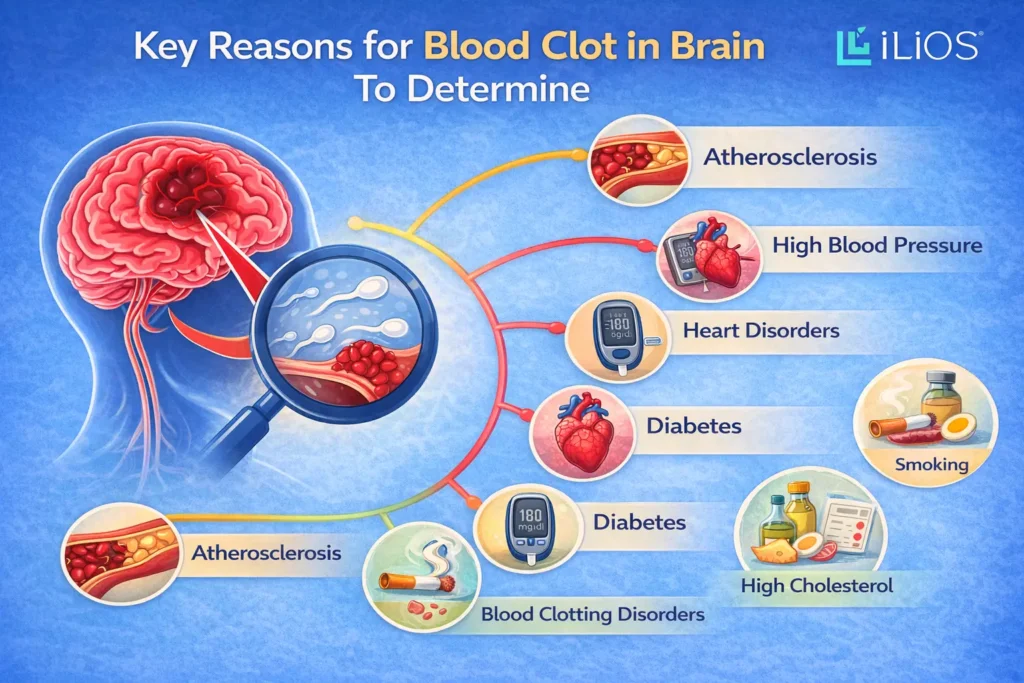
- Atherosclerosis (Blocked Arteries): Fat deposits called plaques may accumulate within the arteries inside the brain or neck, causing the arteries to narrow. A blood clot can occur if the plaque ruptures.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): When blood pressure is consistently high, it affects the blood vessels. This causes them to stiffen and shrink. This can lead to clots forming and to Ischemic stroke.
- Heart Disorders (e.g., Atrial Fibrillation): An irregular heartbeat is one of the blood clots in brain causes, which travel through the bloodstream and lodge in an artery, blocking it.
- Diabetes: Most commonly, high levels of blood sugar activate the blood vessels; as a result, diabetes renders individuals susceptible to developing blood clots in the brain.
- Smoking: It affects the blood vessels, makes the blood thick, and increases the possibility of blood clotting. It reduces the amount of oxygen received in the brain. This is another effect that can cause a stroke.
- High Cholesterol: Having high amounts of low-density lipoprotein, or ‘bad’ cholesterol, contributes to the development of plaques in the artery walls. A constricted artery could then lead to clots that block blood flow.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: In some cases, blood clots form more than usual, which may lead to conditions such as cerebral thrombosis or venous sinus thrombosis.
What are the Standard Blood Clot In Brain Treatment Methods?
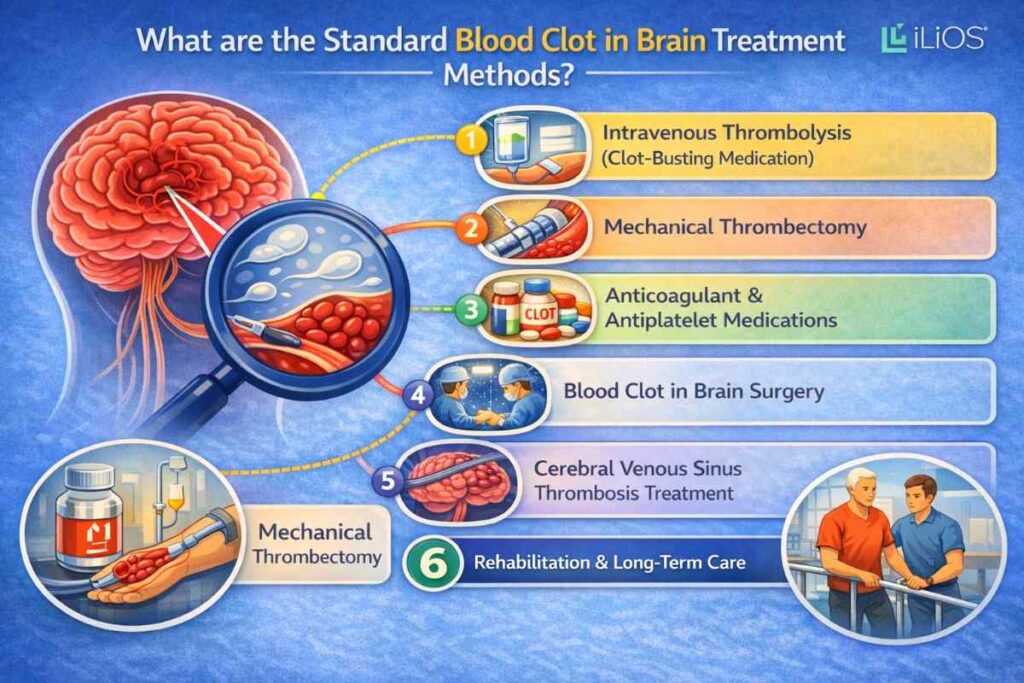
1. Intravenous Thrombolysis (Clot-Busting Medication)
A blocked artery creates the medical condition that requires this treatment as the primary option for an Ischemic stroke. Doctors administer a clot-dissolving drug called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) via an IV. It typically works by breaking down the clot and restoring blood flow to the affected part of the brain.
For best outcomes, this treatment should be administered within 3 to 4.5 hours of symptom onset. Early treatment improves the blood clot in brain survival rate and minimises long-term disability.
2. Mechanical Thrombectomy
In cases of large-artery blockages, doctors may perform a minimally invasive procedure called mechanical thrombectomy. A catheter is inserted through an artery (in the groin) and guided to the brain to physically remove the clot.
This process is performed within 6 to 24 hours of diagnosing the symptom, depending on the imaging results. It has ultimately improved outcomes for severe strokes and can prevent the need for more invasive blood clot in brain surgery in specific cases.
3. Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Medications
Blood thinners that may be used include clopidogrel, aspirin, or anticoagulants that may be in the form of heparin or warfarin. These may be used to manage conditions such as atrial fibrillation or CVST.
These may not dissolve the clot immediately, but they reduce the possibility of recurrence and improve recovery. Complete monitoring by a neurologist is essential when using these drugs.
4. Blood Clot in Brain Surgery
When medications and minimally invasive processes aren’t sufficient, surgery may be required. Surgery options range from decompressive craniectomy, in which part of the skull is removed, to the removal of the clot.
Surgery is an option in cases of brain swelling, a clot causing life-threatening pressure inside the skull, or as a consequence of hemorrhagic transformation. Timely intervention has an important role in the improvement of the rate of survival of blood clots in the brain
5. Treatment for Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST)
For clots in the venous sinuses of the brain, the primary treatment is anticoagulation therapy, even in cases of minor bleeding. Except in very severe cases, it may be impossible to relieve it through endovascular treatments.
In addition, early diagnosis, which may be assisted by imaging techniques, is essential. A Neurology Second Opinion from our experts will enable you to ensure your treatment plan is correct, and you receive the best possible outcome.
6. Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care
After your emergency, rehabilitation is considered one of the most vital parts of your recovery. Rehabilitation is provided through physical, occupational, and speech therapy, as well as cognitive rehabilitation. Depending on the areas of the body that are affected.
Proper and timely care during and after the stroke improves the rate of recovery. It also increases the overall survival rate of blood clots that form during a stroke. Regular checkups with a Neurologist Help ensure effective management and prevention of future stroke.

Serious About Your Health? We Are Too.
Partner with India's fastest-growing diagnostic network for precision testing.
Final Takeaway!
A blood clot in brain can progress rapidly and cause permanent damage if not treated promptly. Suffering from weakness in any part of the body, severe headaches, and difficulty speaking or seeing should not be taken lightly. However, getting immediate medical care may be beneficial.
If any unusual symptoms appear in you or your loved ones, consulting a specialist immediately and seeking an online medical second opinion with Illios would be advisable to make an accurate diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the early symptoms of a brain clot?
Symptoms include sudden weakness, difficulty speaking, drooping of the facial muscles, vision problems, a severe headache, and loss of balance.
2. Is a blood clot in the brain curable?
Yes, early medical treatment, such as clot-busting drugs or procedures, can be beneficial and significantly improve outcomes.
3. Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of recurrence of brain blood clots?
Controlling blood pressure, exercising regularly, managing diabetes, and not smoking can reduce the risk.
4. How quickly do brain clot symptoms appear?
Symptoms typically appear suddenly and without warning. They can develop within seconds to minutes, which is why immediate medical attention is critical.
5. What is the survival rate for brain clots?
The survival rate depends on how quickly treatment is received. When treated within the first 3-4 hours, the chances of survival and recovery improve significantly. Delayed treatment increases the risk of permanent disability or death.
6. How is a brain clot diagnosed?
Doctors use imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI scans, or angiography to detect blood clots in the brain. Blood tests may also be performed to check for clotting disorders.
7. What happens if a brain clot is left untreated?
Without prompt treatment, brain cells continue to die rapidly due to lack of oxygen. This can lead to permanent brain damage, severe disability, loss of bodily functions, or death.
8. How long does recovery from a brain clot take?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the clot and how quickly treatment was received. Some people recover within weeks, while others may need months or years of rehabilitation. Ongoing physical, speech, and occupational therapy are often necessary.
9. Can young people get blood clots in the brain?
Yes, while brain clots are more common in older adults, younger people can also develop them, especially if they have risk factors like blood clotting disorders, heart conditions, high blood pressure, or use certain medications like birth control pills.
10. When should I call emergency services?
Call emergency services immediately if you or someone experiences sudden weakness, facial drooping, difficulty speaking, severe headache, vision problems, or loss of balance. Remember: time is brain—every minute counts.